This article covers the basics of multithreading in Python programming language. Just like multiprocessing, multithreading is a way of achieving multitasking. In multithreading, the concept of threads is used. Let us first understand the concept of thread in computer architecture.
Thread
In computing, a process is an instance of a computer program that is being executed. Any process has 3 basic components:
- An executable program.
- The associated data needed by the program (variables, work space, buffers, etc.)
- The execution context of the program (State of process)
A thread is an entity within a process that can be scheduled for execution. Also, it is the smallest unit of processing that can be performed in an OS (Operating System). In simple words, a thread is a sequence of such instructions within a program that can be executed independently of other code. For simplicity, you can assume that a thread is simply a subset of a process! A thread contains all this information in a Thread Control Block (TCB):
- Thread Identifier: Unique id (TID) is assigned to every new thread
- Stack pointer: Points to thread’s stack in the process. Stack contains the local variables under thread’s scope.
- Program counter: a register which stores the address of the instruction currently being executed by thread.
- Thread state: can be running, ready, waiting, start or done.
- Thread’s register set: registers assigned to thread for computations.
- Parent process Pointer: A pointer to the Process control block (PCB) of the process that the thread lives on.
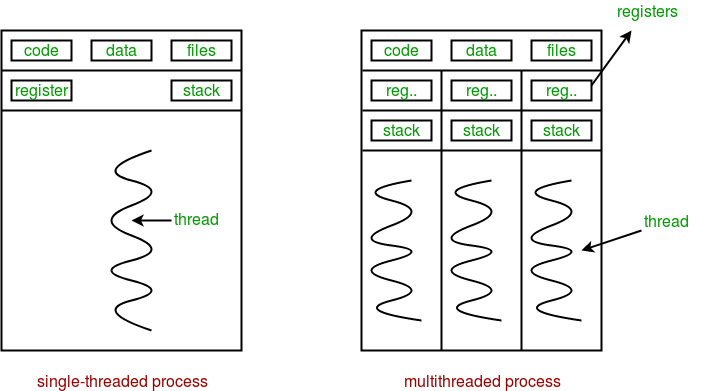
Consider the diagram below to understand the relationship between the process and its thread:

Multi-threading: Multiple threads can exist within one process where:
- Each thread contains its own register set and local variables (stored in stack).
- All threads of a process share global variables (stored in heap) and the program code.
Consider the diagram below to understand how multiple threads exist in memory:
Multithreading is defined as the ability of a processor to execute multiple threads concurrently.
In a simple, single-core CPU, it is achieved using frequent switching between threads. This is termed as context switching. In context switching, the state of a thread is saved and state of another thread is loaded whenever any interrupt (due to I/O or manually set) takes place. Context switching takes place so frequently that all the threads appear to be running parallelly (this is termed as multitasking).

Consider the diagram below in which a process contains two active threads:
Multi-threading in Python
In Python, the threading module provides a very simple and intuitive API for spawning multiple threads in a program. Let us consider a simple example using a threading module:
- Python3
# Python program to illustrate the concept# of threading# importing the threading moduleimport threadingdef print_cube(num): # function to print cube of given num print("Cube: {}" .format(num * num * num))def print_square(num): # function to print square of given num print("Square: {}" .format(num * num))if __name__ =="__main__": # creating thread t1 = threading.Thread(target=print_square, args=(10,)) t2 = threading.Thread(target=print_cube, args=(10,)) # starting thread 1 t1.start() # starting thread 2 t2.start() # wait until thread 1 is completely executed t1.join() # wait until thread 2 is completely executed t2.join() # both threads completely executed print("Done!") |
Square: 100 Cube: 1000 Done!
Let us try to understand the above code:
- To import the threading module, we do:
import threading
- To create a new thread, we create an object of Thread class. It takes following arguments:
- target: the function to be executed by thread
- args: the arguments to be passed to the target function
- To start a thread, we use start method of Thread class.
t1.start() t2.start()
- Once the threads start, the current program (you can think of it like a main thread) also keeps on executing. In order to stop execution of current program until a thread is complete, we use join method.
t1.join() t2.join()
- As a result, the current program will first wait for the completion of t1 and then t2. Once, they are finished, the remaining statements of current program are executed.
Consider the diagram below for a better understanding of how above program works:

Consider the python program given below in which we print thread name and corresponding process for each task:
- Python3
# Python program to illustrate the concept# of threadingimport threadingimport osdef task1(): print("Task 1 assigned to thread: {}".format(threading.current_thread().name)) print("ID of process running task 1: {}".format(os.getpid()))def task2(): print("Task 2 assigned to thread: {}".format(threading.current_thread().name)) print("ID of process running task 2: {}".format(os.getpid()))if __name__ == "__main__": # print ID of current process print("ID of process running main program: {}".format(os.getpid())) # print name of main thread print("Main thread name: {}".format(threading.current_thread().name)) # creating threads t1 = threading.Thread(target=task1, name='t1') t2 = threading.Thread(target=task2, name='t2') # starting threads t1.start() t2.start() # wait until all threads finish t1.join() t2.join() |
ID of process running main program: 11758 Main thread name: MainThread Task 1 assigned to thread: t1 ID of process running task 1: 11758 Task 2 assigned to thread: t2 ID of process running task 2: 11758
Let us try to understand the above code:
- We use os.getpid() function to get ID of current process.
print("ID of process running main program: {}".format(os.getpid()))
- As it is clear from the output, the process ID remains the same for all threads.
- We use threading.main_thread() function to get the main thread object. In normal conditions, the main thread is the thread from which the Python interpreter was started. name attribute of thread object is used to get the name of thread.
print("Main thread name: {}".format(threading.main_thread().name))
- We use the threading.current_thread() function to get the current thread object.
print("Task 1 assigned to thread: {}".format(threading.current_thread().name))
The diagram given below clears the above concept:

So, this was a brief introduction to multithreading in Python. The next article in this series covers synchronization between multiple threads. Multithreading in Python | Set 2 (Synchronization)
This article is contributed by Nikhil Kumar. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using write.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
Using a thread pool:
A thread pool is a collection of threads that are created in advance and can be reused to execute multiple tasks. The concurrent.futures module in Python provides a ThreadPoolExecutor class that makes it easy to create and manage a thread pool.
In this example, we define a function worker that will run in a thread. We create a ThreadPoolExecutor with a maximum of 2 worker threads. We then submit two tasks to the pool using the submit method. The pool manages the execution of the tasks in its worker threads. We use the shutdown method to wait for all tasks to complete before the main thread continues.
. Multithreading can help you make your programs more efficient and responsive. However, it’s important to be careful when working with threads to avoid issues such as race conditions and deadlocks.
- Python3
import concurrent.futuresdef worker(): print("Worker thread running")# create a thread pool with 2 threadspool = concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=2)# submit tasks to the poolpool.submit(worker)pool.submit(worker)# wait for all tasks to completepool.shutdown(wait=True)print("Main thread continuing to run") |
Output
Worker thread running Worker thread running Main thread continuing to run
